Neste artigo é demonstrado como programar um Arduino para controlar uma fita de LED RGB endereçável.
Com este tutorial é possível criar inúmeros tipos de efeitos luminosos apenas com o Arduino.

Componentes Utilizados
- Arduino Uno/Mega
- Cabo USB para Arduino
- Vários jumpers
- Resistor 330 ohm
- Fonte 5v 1A
- Fita de LED RGB Endereçável
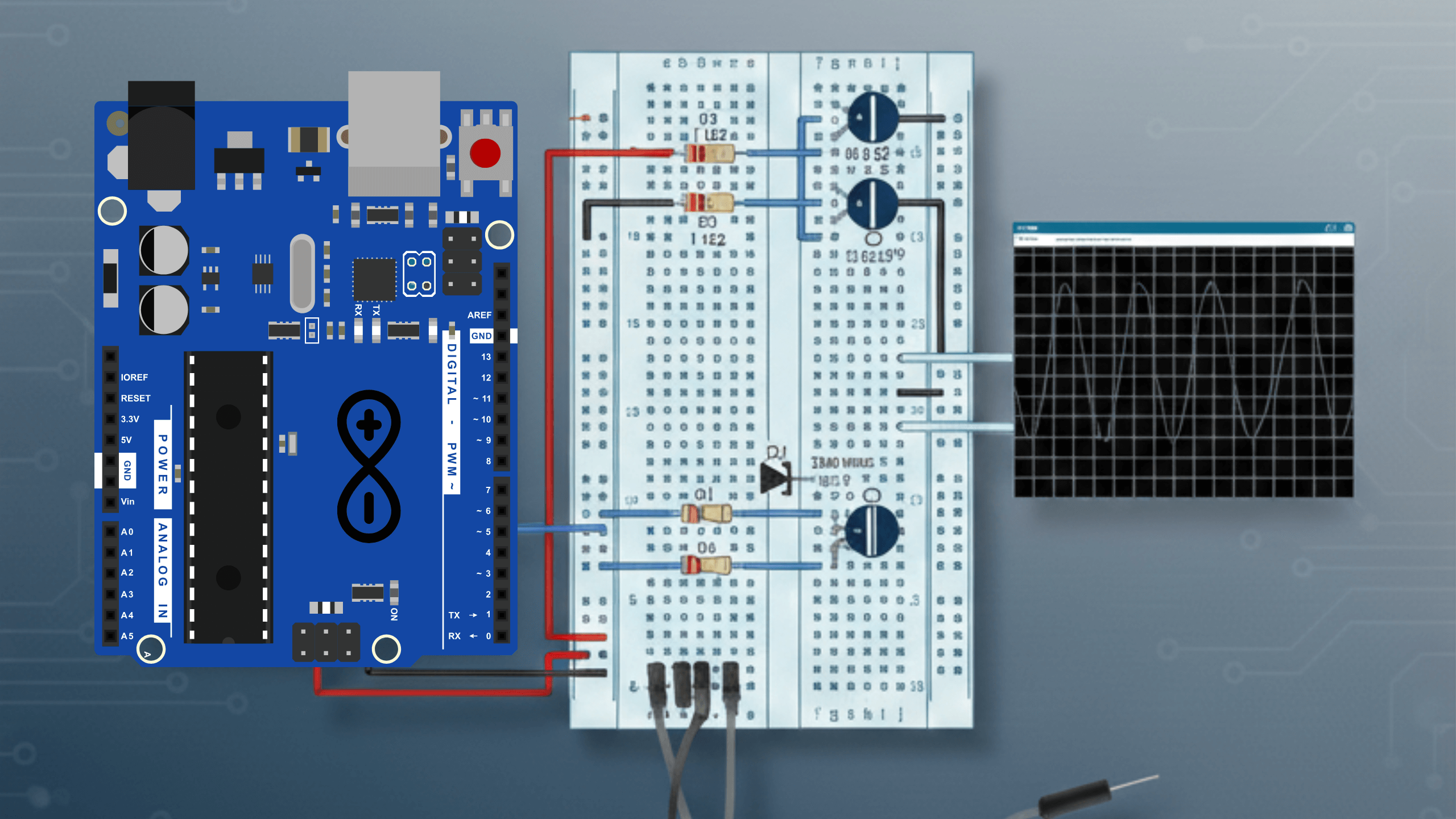
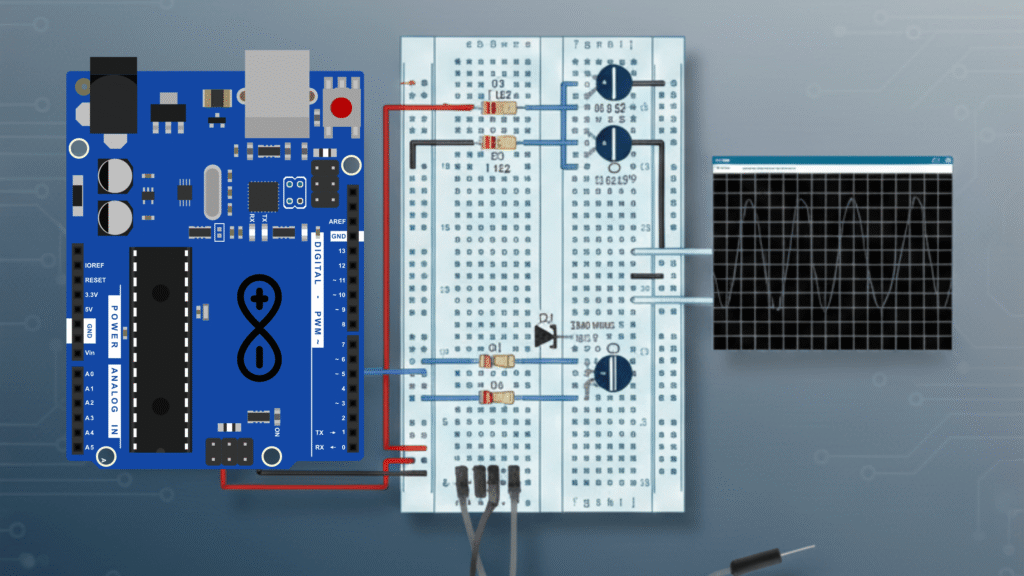
Esquemático

Código Utilizado
Apenas copie e cole o código abaixo na IDE Arduino e baixe a biblioteca FastLED.h (no fim do artigo) para funcionamento completo do código:
#include <FastLED.h>
FASTLED_USING_NAMESPACE
#if defined(FASTLED_VERSION) && (FASTLED_VERSION < 3001000)
#warning "Requires FastLED 3.1 or later; check github for latest code."
#endif
#define DATA_PIN 3 //pino do arduino conectado a fita de LEDS WS2812B
//#define CLK_PIN 4 //Nao utilizado na fita WS2812B
#define LED_TYPE WS2812B
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB //Ordem das cores na fita de led WS2812B
#define NUM_LEDS 30 //numero de leds na fita
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
#define BRIGHTNESS 96 //brilho dos leds 0 a 255
#define FRAMES_PER_SECOND 120 //frames por segundo, quanto mais leds na fita menor deve ser a taxa de frames por segundo
void setup() {
delay(3000); // 3 second delay for recovery
// tell FastLED about the LED strip configuration
FastLED.addLeds<LED_TYPE,DATA_PIN,COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection(TypicalLEDStrip);
//FastLED.addLeds<LED_TYPE,DATA_PIN,CLK_PIN,COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection(TypicalLEDStrip);
// set master brightness control
FastLED.setBrightness(BRIGHTNESS);
}
// List of patterns to cycle through. Each is defined as a separate function below.
typedef void (*SimplePatternList[])();
SimplePatternList gPatterns = { rainbow, rainbowWithGlitter, confetti, sinelon, juggle, bpm };
uint8_t gCurrentPatternNumber = 0; // Index number of which pattern is current
uint8_t gHue = 0; // rotating "base color" used by many of the patterns
void loop()
{
// Call the current pattern function once, updating the 'leds' array
gPatterns[gCurrentPatternNumber]();
// send the 'leds' array out to the actual LED strip
FastLED.show();
// insert a delay to keep the framerate modest
FastLED.delay(1000/FRAMES_PER_SECOND);
// do some periodic updates
EVERY_N_MILLISECONDS( 20 ) { gHue++; } // slowly cycle the "base color" through the rainbow
EVERY_N_SECONDS( 10 ) { nextPattern(); } // change patterns periodically
}
#define ARRAY_SIZE(A) (sizeof(A) / sizeof((A)[0]))
void nextPattern()
{
// add one to the current pattern number, and wrap around at the end
gCurrentPatternNumber = (gCurrentPatternNumber + 1) % ARRAY_SIZE( gPatterns);
}
void rainbow()
{
// FastLED's built-in rainbow generator
fill_rainbow( leds, NUM_LEDS, gHue, 7);
}
void rainbowWithGlitter()
{
// built-in FastLED rainbow, plus some random sparkly glitter
rainbow();
addGlitter(80);
}
void addGlitter( fract8 chanceOfGlitter)
{
if( random8() < chanceOfGlitter) {
leds[ random16(NUM_LEDS) ] += CRGB::White;
}
}
void confetti()
{
// random colored speckles that blink in and fade smoothly
fadeToBlackBy( leds, NUM_LEDS, 10);
int pos = random16(NUM_LEDS);
leds[pos] += CHSV( gHue + random8(64), 200, 255);
}
void sinelon()
{
// a colored dot sweeping back and forth, with fading trails
fadeToBlackBy( leds, NUM_LEDS, 20);
int pos = beatsin16( 13, 0, NUM_LEDS-1 );
leds[pos] += CHSV( gHue, 255, 192);
}
void bpm()
{
// colored stripes pulsing at a defined Beats-Per-Minute (BPM)
uint8_t BeatsPerMinute = 62;
CRGBPalette16 palette = PartyColors_p;
uint8_t beat = beatsin8( BeatsPerMinute, 64, 255);
for( int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) { //9948
leds[i] = ColorFromPalette(palette, gHue+(i*2), beat-gHue+(i*10));
}
}
void juggle() {
// eight colored dots, weaving in and out of sync with each other
fadeToBlackBy( leds, NUM_LEDS, 20);
byte dothue = 0;
for( int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
leds[beatsin16( i+7, 0, NUM_LEDS-1 )] |= CHSV(dothue, 200, 255);
dothue += 32;
}
}
Downloads
Baixe o código e biblioteca utilizada aqui.
Para saber como montar o projeto na prática, assista o vídeo tutorial abaixo: